SAP BAPI Overview
Mule runtime supports SAP integration through our Anypoint Connector for SAP, an SAP-certified Java connector that leverages the SAP Java Connector (JCo) libraries, thus allowing Mule applications to:
-
Execute BAPI functions over the RFC protocol, supporting the following types:
-
Synchronous RFC (sRFC)
-
Transactional RFC (tRFC)
-
Queued RFC (qRFC)
-
-
Act as a JCo Server to be called as a BAPI over sRFC, tRFC, and qRFC.
-
Send IDocs over tRFC and qRFC.
-
Receive IDocs over tRFC and qRFC.
-
Transform SAP objects (JCo Function/BAPI & IDocs) to and from XML.
For this guide, we’ll walk through the process of setting up the SAP Connector to execute a BAPI function over RFC.
1. Setup HTTP Connector
1.1 Open Studio and create a new Mule Project
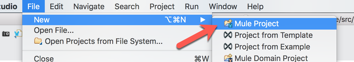
1.2 In the New Mule Project window, give the project a name (e.g. workshop-sap), select a Runtime, and then click on Finish
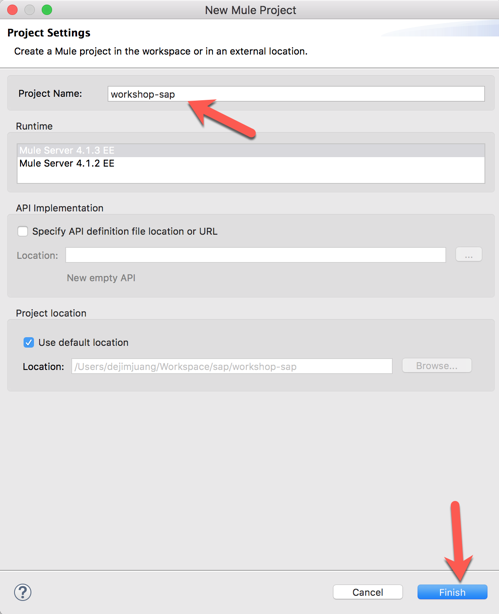
1.3 Once the new project is created, you’ll be presented with a blank canvas.
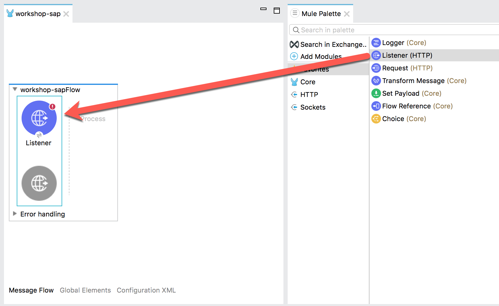
In the Mule Palette on the right, click on HTTP and then drag and drop the Listener into the canvas 1.4 If the Mule Properties tab doesn’t open, click the Listener icon and click on the green plus sign to create a new Connector configuration.
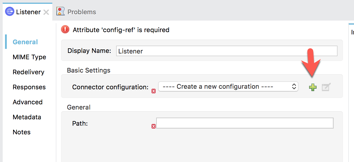
1.5 Under the General tab, and in the Connection section, fill in the host and the port with the following:
Host: 0.0.0.0 Port: 8081
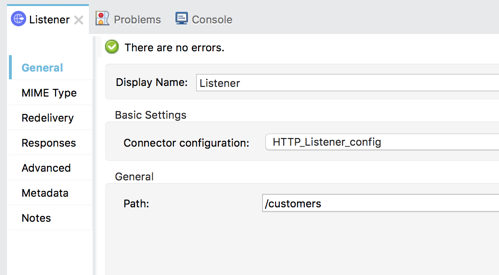
And then click on OK 1.6 Back in the Listener Mule properties tab, fill in the Path field with the following:

/customers
2. Configure SAP Connector
2.1 Back in the Mule Palette, we need to add the SAP Connector.
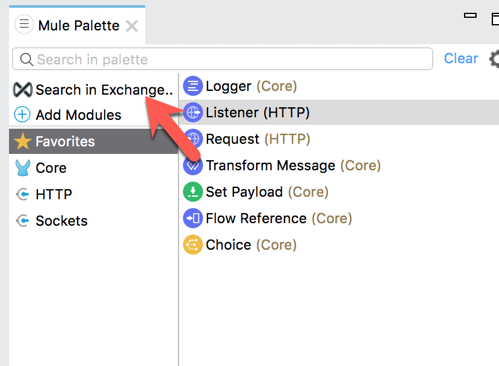
Click on Search in Exchange
2.2 In the Add Modules to Project window, type in ‘sap’ for the search term (1)
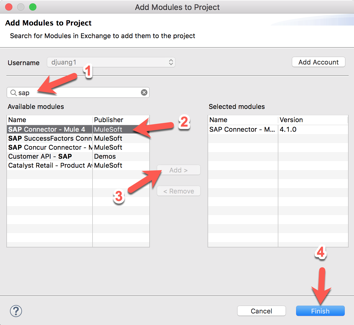
In the Available modules (2) select SAP Connector - Mule 4 and click on Add (3)
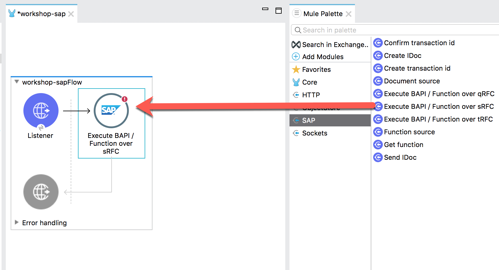
Click on Finish (4) to add the module to the project. 2.3 From the list of operations from SAP, drag and drop the Execute BAPI / Function over sRFC onto the canvas. Place it after the Listener module.
2.4 For this guide, we’ll configure properties in a seperate configuration file.
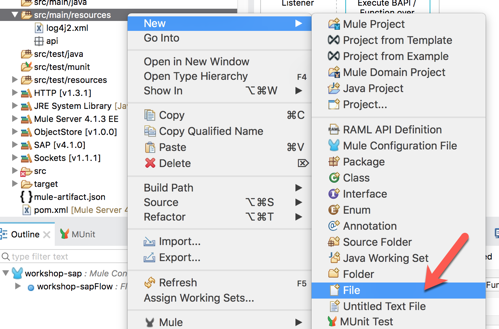
Right-click on the src/main/resources folder and select New > File and name the file app.properties
2.5 Copy and past the following into the newly create file. Populate the properties with the credentials and settings for your SAP instance.
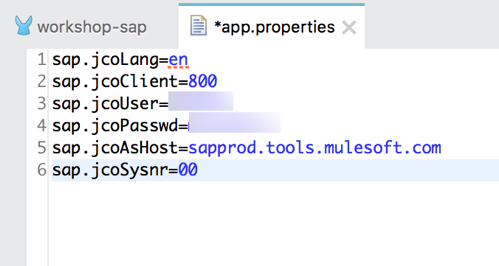
If needed, you can use the credentials below from our sandbox instance. Contact the instructor for the login and password.
-
sap.jcoLang=en
-
sap.jcoClient=800
-
sap.jcoUser=
-
sap.jcoPasswd=
-
sap.jcoAsHost=your-sap-host-or-ip.com
-
sap.jcoSysnr=00
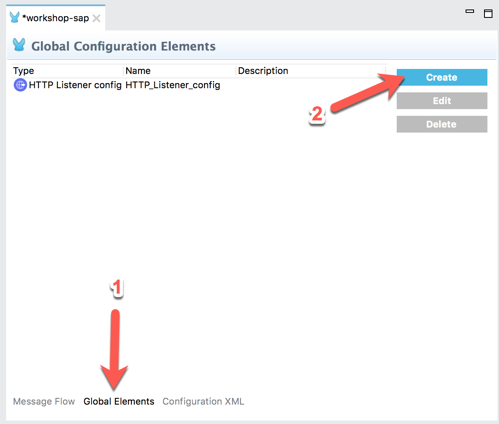
2.6 In the canvas, click on Global Elements (1) and then click on Create (2)
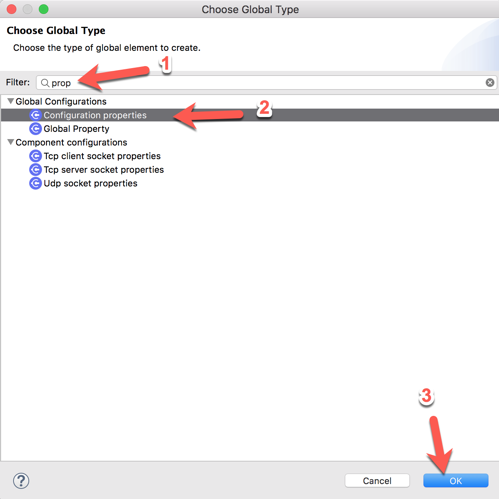
2.7 In the Filter, type in ‘prop’ (1) and select Configuration properties (2) and then click on OK (3)
2.8 In the Configuration properties, click on the browse file button (1).
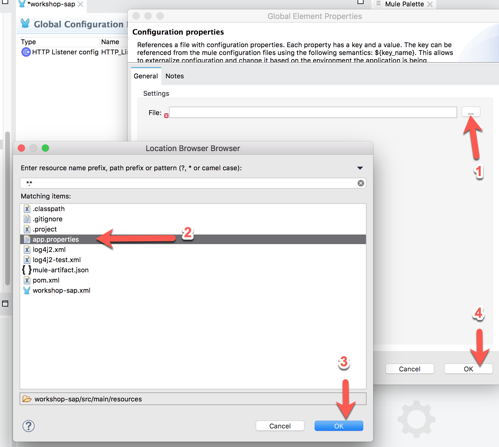
Locate and select the app.properties file you created (2) and then click on OK (3)
Back on the previous window, click on OK to save your changes (4).
2.9 Let’s go back to the SAP Connector and use those properties to connect.
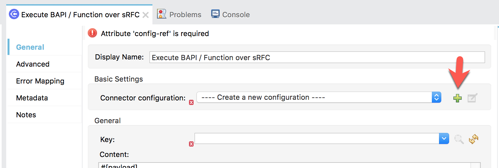
In the Execute BAPI / Function over sRFC module, click on the green plus sign to configure the Connector configuration
2.10 In the SAP Outbound window, click on the Confgure button next to the iDoc Library field.
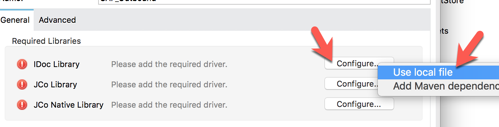
Select Use local file
2.11 In the Choose local file, click on Browse and point it to the sapidoc3.jar file.
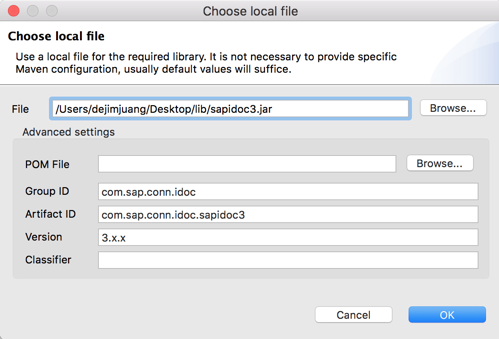
Keep the default settings and click on OK 2.12 Back in the SAP Outbound window, there should be a green checkmark next to the iDoc Library field.
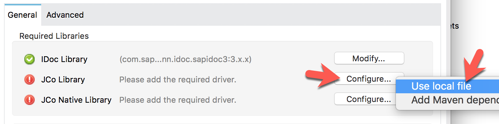
Next, let’s add the JCo Library. Click on Configure and select Use local file 2.13 In the Choose local file, click on Browse and point it to the sapjco3.jar file.
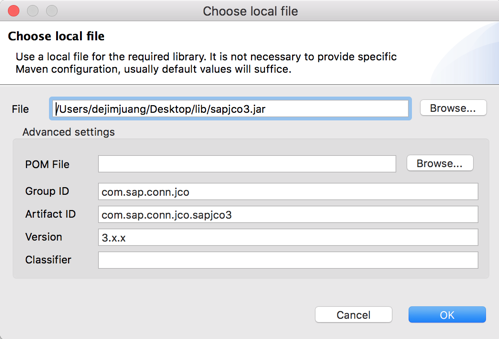
Keep the default settings and click on OK 2.14 Back in the SAP Outbound window, there should be a green checkmark next to the JCo Library field.
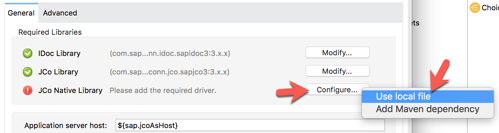
Next, let’s add the JCo Native Library. Click on Configure and select Use local file 2.15 For the JCO native libraries, they are platform specific. When you go to browse and select the files, besure to change the dropdown to the specific extension you’re looking for. Once you select the file, click on Open
JCo Platform-specific native libraries: Windows - sapjco3.dll Mac OS - libsapjco3.jnilib Linux - libsapjco3.so
2.16 Keep the default settings on the Choose local file window and click on OK
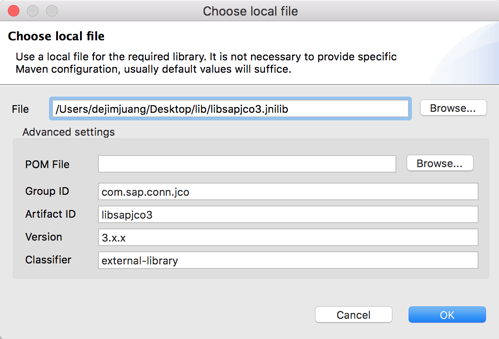
2.17 Back in the SAP Outbound window, all the required libraries should be green now.
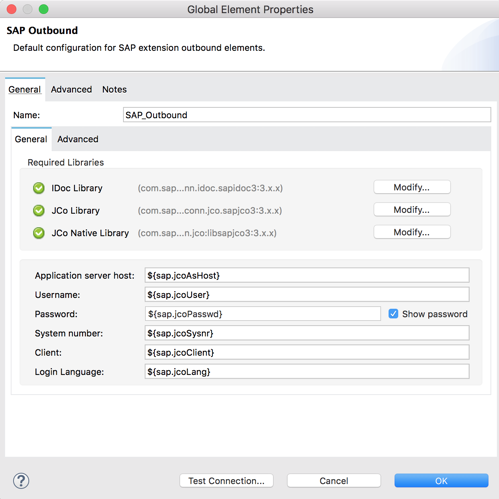
Fill in the remaining fields with the corresponding property placeholders below.
Application server host: |
${sap.jcoAsHost} |
Username: |
${sap.jcoUser} |
Password: |
${sap.jcoPasswd} |
System number: |
${sap.jcoSysnr} |
Client: |
${sap.jcoClient} |
Login Language: |
${sap.jcoLang} |
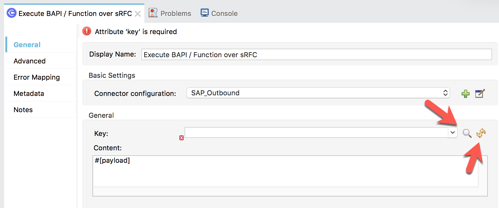
Click on Test Connection to make sure eveything has been configured correctly before clicking on OK. 2.18 Back on the Execute BAPI / Function over sRFC tab, click on the refresh button next to the Key field. Once it refreshes, click on the magnifying glass icon next to it.
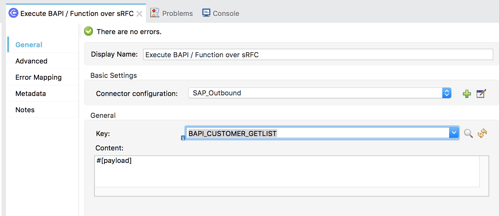
2.19 In the search field, type in BAPI_CUSTOMER_GET and then select the BAPI_CUSTOMER_GETLIST item from the matching items list.
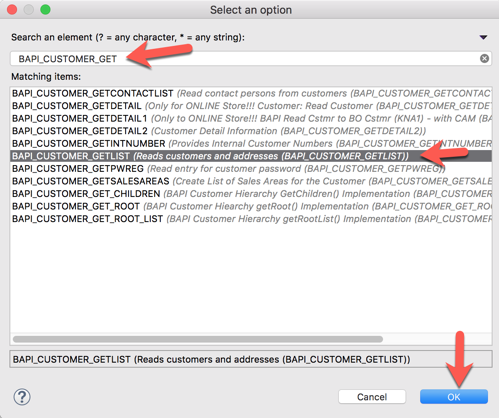
Click OK.
2.20 If you know the name of the BAPI you want to use from your system, you can type that into the Key field as well.
3. Use DataWeave to Create a BAPI Function
3.1 Now that the SAP Connector is configured with the correct credentials and BAPI we intend to use, we need to setup the message to pass in.
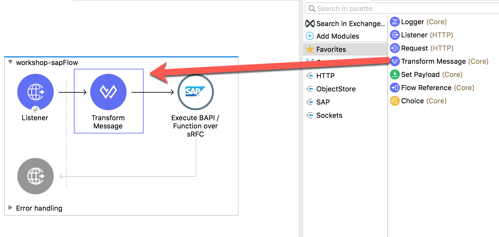
In the Mule Palette, find and drag and drop the Transform Message component into the canvas. Drop it between the Listener and the Execute BAPI / Function over sRFC module 3.2 In the Transform Message tab, you can see how the component provides metadata around the output.
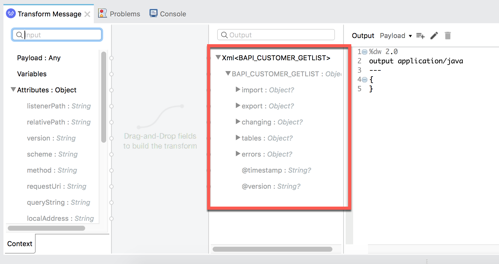
3.3 Let’s make some modifications to the message. First, we’ll set the maximum number of rows to return from SAP.
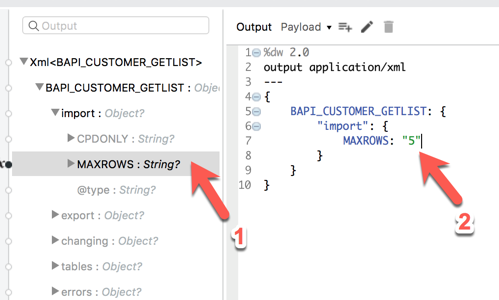
Under the import node, double-click on MAXROWS
Notice how the DataWeave script is generated. Change null to “5” and be sure to keep the double quotes.
3.4 Next we need the ID range of customer records we want returned:
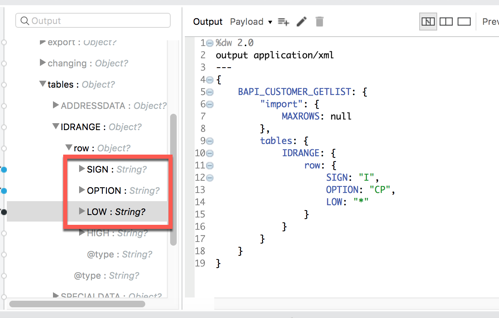
Under the tables node, add the following lines:
-
SIGN “I”
-
OPTION “CP”
-
LOW “*”
3.5 The final DataWeave should look like the following below. You can also copy and paste the script into Studio as well:
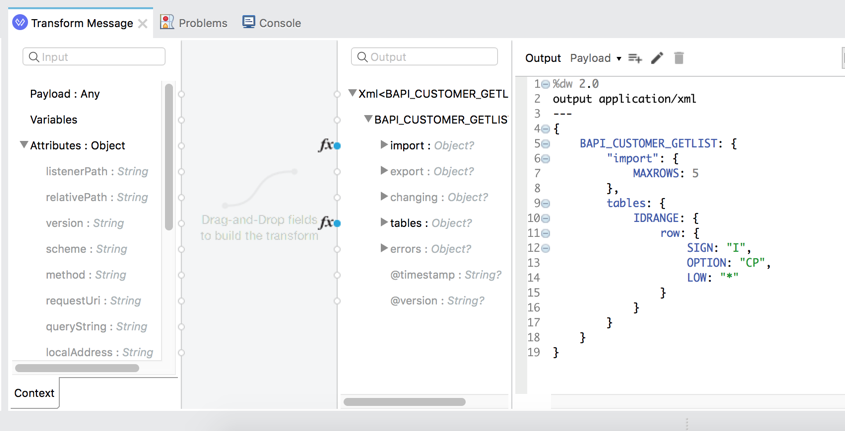
%dw 2.0 output application/xml --- { BAPI_CUSTOMER_GETLIST: { "import": { MAXROWS: 5 }, tables: { IDRANGE: { row: { SIGN: "I", OPTION: "CP", LOW: "*" } } } } }
4. Transform output to JSON
4.1 Once the SAP Connector processes the function, the data will be returned as XML. Let’s go ahead and transform that and output the customer list as JSON data.
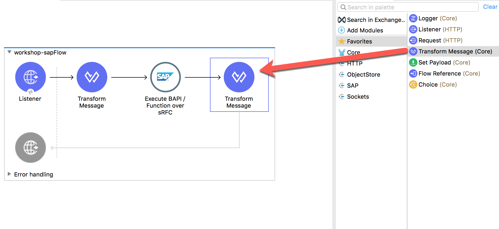
From the Mule Palette drag and drop a Transform Message module into the canvas. Place it after the Execute BAPI / Function over sRFC 4.2 In the Mule Properties tab for the Transform Message component, modify the DataWeave script and paste the following:
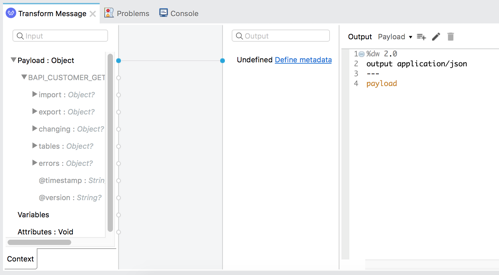
%dw 2.0 output application/json --- payload
5. Test Project
5.1 Our next step is to test the flow we’ve built. In the Package Explorer, right click on the canvas and Run project workshop-sap
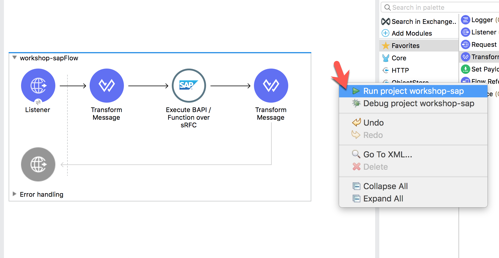
5.2 The Console tab should pop-up now. Wait for the status to show DEPLOYED before moving onto the next step.
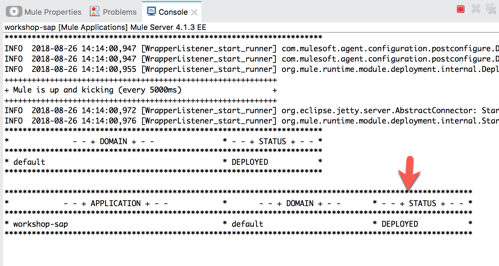
5.3 Let’s test out our flow now. Switch to Google Chrome and enter the following URL:
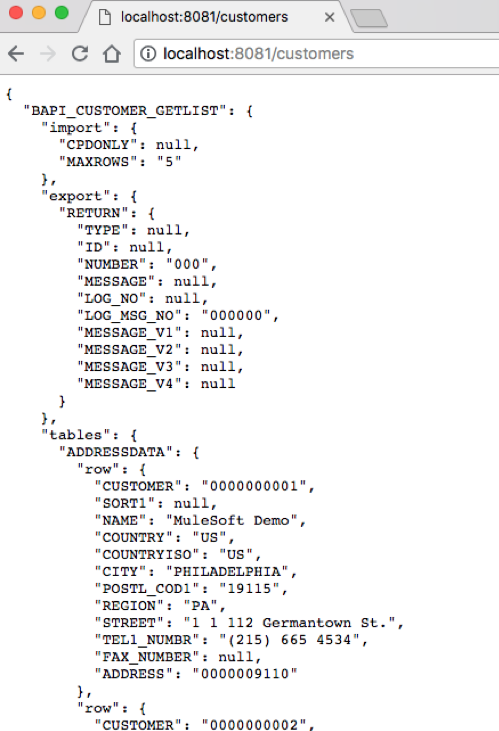
Let’s test it out: http://localhost:8081/customers
If everything was configured correctly, you should see the following screen on the right.